Unraveling the Efficiency of Windows 11’s Fast Boot Process
Related Articles: Unraveling the Efficiency of Windows 11’s Fast Boot Process
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Efficiency of Windows 11’s Fast Boot Process. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Efficiency of Windows 11’s Fast Boot Process

Windows 11, the latest iteration of Microsoft’s operating system, boasts a myriad of features designed to enhance user experience. Among these is the "fast boot" process, a streamlined approach to system startup that significantly reduces the time required for users to access their desktops. This article delves into the intricacies of this feature, exploring its underlying mechanisms, benefits, and potential considerations.
The Mechanics of Fast Boot
Windows 11’s fast boot process, often referred to as "hybrid shutdown," employs a clever strategy that combines the speed of traditional cold booting with the convenience of a quick resume. It achieves this by leveraging a hybrid approach that involves:
- Saving System State: When a user initiates a "shutdown" in Windows 11, the system does not completely power down. Instead, it saves the current state of the operating system, including open applications and user settings, to a hibernation file on the hard drive.
- Fast Boot Sequence: Upon restarting, Windows 11 skips the lengthy process of loading the operating system from scratch. Instead, it directly accesses the saved system state from the hibernation file, restoring the user’s environment almost instantly.
This approach effectively bypasses the time-consuming procedures associated with a full system boot, such as loading drivers and initializing hardware components. As a result, users experience a noticeable reduction in boot time, allowing them to access their systems and resume their work more quickly.
Benefits of Fast Boot
The fast boot feature in Windows 11 offers several advantages to users, enhancing both efficiency and user experience:
- Reduced Boot Time: The most significant benefit of fast boot is the dramatic reduction in the time it takes for the system to start up. This translates to a more responsive and user-friendly experience, especially for users who frequently restart their computers.
- Enhanced Productivity: By minimizing the time spent waiting for the system to boot, fast boot promotes productivity. Users can quickly access their applications and resume their work, minimizing interruptions and maximizing time spent on productive tasks.
- Improved User Experience: The seamless and rapid boot process contributes to a more enjoyable user experience. Users are less likely to feel frustrated by lengthy startup times, leading to a more positive interaction with their computers.
- Energy Efficiency: While fast boot does not eliminate power consumption during shutdown, it significantly reduces the time the system spends in a high-power state. This can lead to modest energy savings, particularly for users who frequently restart their computers.
Considerations Regarding Fast Boot
While fast boot offers numerous benefits, it’s important to acknowledge potential considerations:
- Potential for Data Loss: In the event of a power outage or system crash during the fast boot process, there is a small risk of data loss. This is because the system is in a partially powered state, and a sudden interruption could disrupt the process of saving system state to the hibernation file.
- Increased Disk Wear: Frequent use of fast boot can lead to increased wear and tear on the hard drive. This is because the system is constantly writing to and reading from the hibernation file, which can accelerate the degradation of the drive over time.
- Compatibility Issues: Some older applications or hardware components may not be fully compatible with fast boot. This can lead to unexpected behavior or even system instability.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do I enable or disable fast boot in Windows 11?
Enabling or disabling fast boot in Windows 11 is a straightforward process:
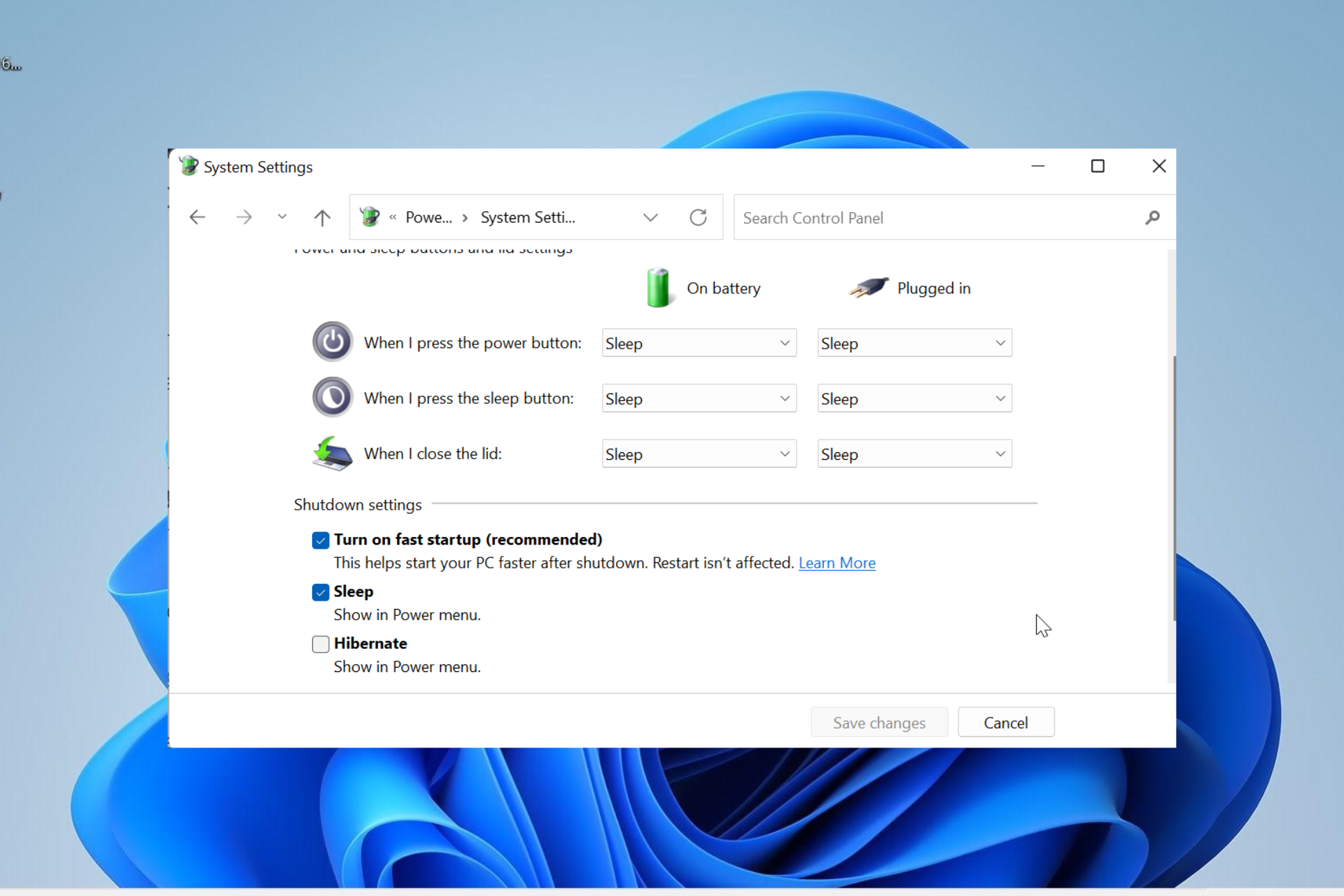
- Open Control Panel: Search for "Control Panel" in the Windows search bar and open it.
- Navigate to Power Options: Click on "Hardware and Sound," followed by "Power Options."
- Choose "Choose what the power buttons do": Click on this option in the left-hand pane.
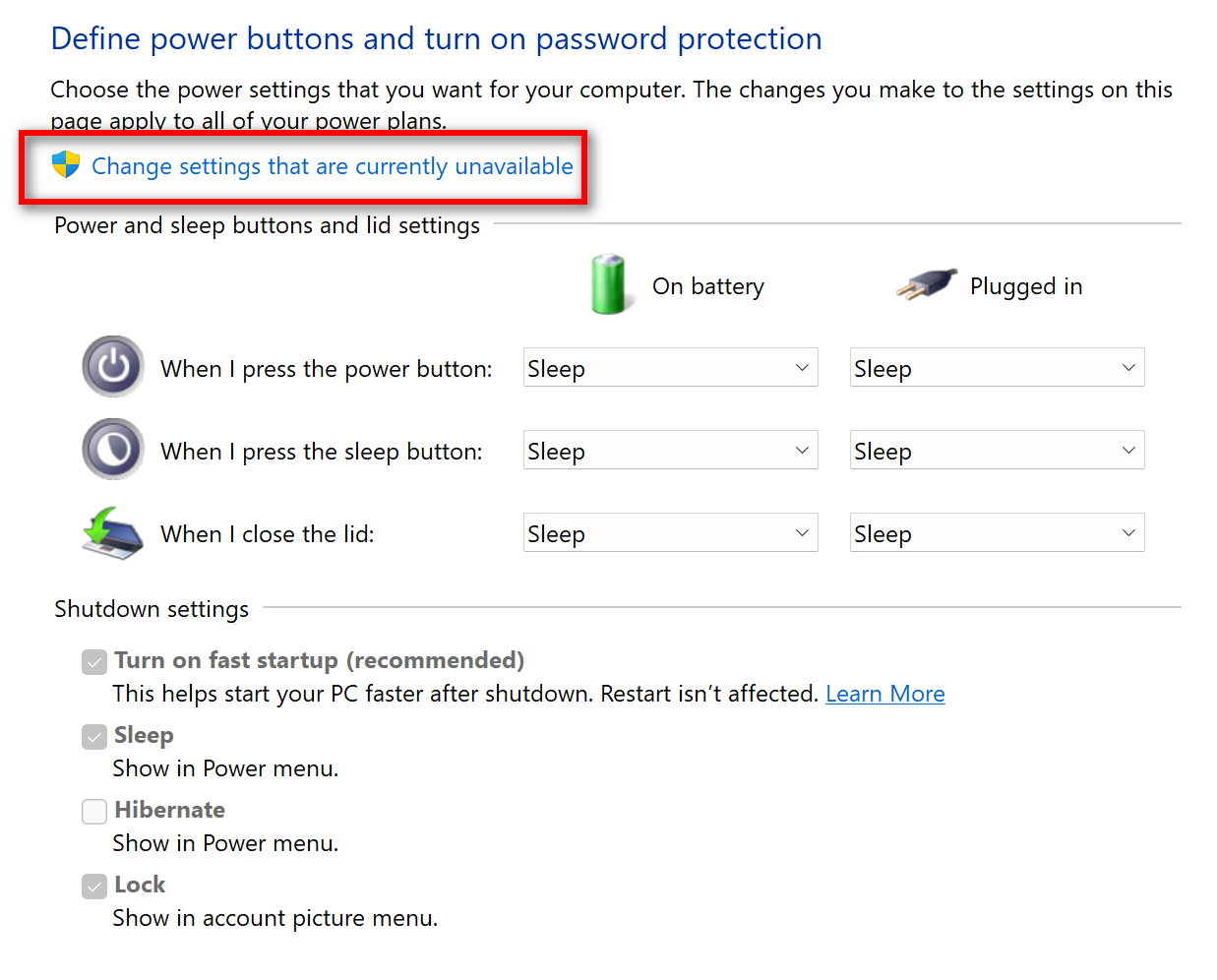
- Select "Change settings that are currently unavailable": This will unlock advanced power options.
- Uncheck or check "Turn on fast startup (recommended)": Unchecking this box will disable fast boot, while checking it will enable it.
2. Does fast boot affect the performance of my computer?
Fast boot does not significantly impact the overall performance of your computer. It primarily affects the time it takes to start up, not the speed of your system once it is running.
3. Is fast boot safe for my data?
While generally safe, fast boot does carry a small risk of data loss in the event of a power outage or system crash during the boot process. However, this risk is relatively low, and the benefits of fast boot typically outweigh this potential concern.
4. Can I disable fast boot if I am experiencing problems?
Yes, you can disable fast boot if you suspect it is causing issues. This will revert the system to a traditional boot process, which may resolve any compatibility problems.
5. What are the best practices for using fast boot?
- Regularly back up your data: This will help mitigate the risk of data loss in the event of a system crash during fast boot.
- Use a reliable power supply: A stable power source will minimize the risk of power outages that could disrupt the fast boot process.
- Monitor your hard drive health: Keep an eye on the health of your hard drive to ensure it is not experiencing excessive wear and tear due to frequent use of fast boot.
Tips for Optimizing Fast Boot
- Minimize the Number of Startup Programs: A large number of startup programs can slow down the boot process. Use the Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc) to identify and disable unnecessary startup programs.
- Defragment Your Hard Drive: A fragmented hard drive can slow down system performance, including boot times. Regularly defragmenting your drive can improve overall system responsiveness.
- Update Your Drivers: Outdated drivers can sometimes cause compatibility issues with fast boot. Ensure that all your drivers are up-to-date for optimal performance.
- Use a Solid-State Drive (SSD): SSDs offer significantly faster read and write speeds compared to traditional hard drives, which can significantly improve boot times.
Conclusion
Windows 11’s fast boot feature is a valuable addition to the operating system, offering a significant improvement in boot times and overall user experience. By leveraging a hybrid approach that combines the speed of cold booting with the convenience of a quick resume, fast boot empowers users to access their systems and resume their work more quickly, enhancing productivity and streamlining their daily workflows. While there are considerations regarding data loss and potential hard drive wear, the benefits of fast boot generally outweigh these concerns. By understanding the mechanics and considerations of this feature, users can leverage its potential to optimize their computing experience and enjoy a more efficient and enjoyable interaction with their Windows 11 systems.





![How to Enable or Turn On Fast Startup on Windows 11 [Tutorial] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/aO2eIvIHUlU/maxresdefault.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Efficiency of Windows 11’s Fast Boot Process. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!