Unlocking the Potential of Remote Assistance: Troubleshooting Windows 11 Quick Assist Issues
Related Articles: Unlocking the Potential of Remote Assistance: Troubleshooting Windows 11 Quick Assist Issues
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unlocking the Potential of Remote Assistance: Troubleshooting Windows 11 Quick Assist Issues. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unlocking the Potential of Remote Assistance: Troubleshooting Windows 11 Quick Assist Issues

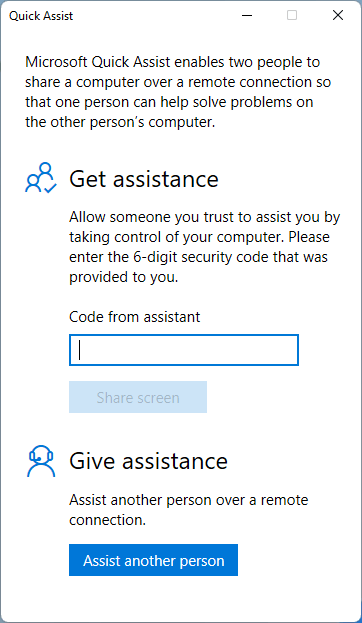
Windows 11’s Quick Assist feature offers a convenient and efficient method for providing remote technical support, enabling users to connect with others and offer assistance in real-time. This powerful tool allows users to remotely control another computer, view their screen, and even share files, making it an invaluable resource for troubleshooting technical difficulties, collaborating on projects, or simply offering assistance to friends and family.
However, like any technology, Quick Assist can occasionally encounter issues, preventing users from accessing its full potential. When Quick Assist fails to function as expected, it can significantly disrupt workflows, hinder collaboration, and create frustration for both the user seeking assistance and the one offering it.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to understanding the common causes of Quick Assist malfunction in Windows 11, offering practical solutions to overcome these obstacles and restore seamless remote assistance functionality.
Understanding the Importance of Quick Assist
Before delving into troubleshooting steps, it is crucial to understand the significance of Quick Assist and its potential benefits. Quick Assist serves as a valuable tool for:
-
Remote Troubleshooting: It enables users to remotely diagnose and resolve technical issues on another computer, eliminating the need for physical presence. This is particularly helpful for situations where users might lack technical expertise or encounter complex problems.
-
Collaborative Work: Quick Assist facilitates seamless collaboration on projects by allowing users to share screens, edit documents, and work together in real-time, regardless of physical location. This fosters efficiency and productivity, especially in remote work environments.
-
Remote Support: Quick Assist empowers individuals to provide technical assistance to friends, family, or colleagues remotely, ensuring timely resolution of issues without the need for physical interaction. This proves invaluable for those who might be less tech-savvy or require assistance with specific tasks.
Common Reasons for Quick Assist Malfunction
While Quick Assist is a powerful tool, it can be susceptible to various issues that hinder its functionality. Some common causes of Quick Assist malfunctions include:
-
Firewall Restrictions: Windows Firewall, a built-in security feature, can sometimes block Quick Assist connections, preventing users from establishing a remote connection. This might occur due to stringent security settings or a misunderstanding of Quick Assist’s legitimate nature.
-
Network Connectivity Issues: Quick Assist relies on a stable internet connection to function properly. Intermittent or weak network signals can disrupt the connection process, leading to failed attempts at establishing a remote session.
-
Compatibility Problems: Outdated drivers or software incompatibilities can sometimes interfere with Quick Assist’s functionality. This might be especially prevalent when using older versions of Windows or outdated hardware components.
-
User Account Permissions: Insufficient user account permissions can prevent Quick Assist from establishing a connection. This is often the case when users lack administrative privileges on their computers, restricting access to certain system functionalities.
-
System Errors or Bugs: Like any software, Quick Assist can occasionally encounter system errors or bugs that hinder its operation. These issues might arise from software glitches, corrupted system files, or other unforeseen circumstances.
Troubleshooting Quick Assist Issues: A Step-by-Step Guide
Addressing Quick Assist malfunctions requires a systematic approach, starting with basic troubleshooting steps and progressively moving towards more advanced solutions. Here’s a comprehensive guide to resolving Quick Assist issues:
1. Verify Network Connectivity:
- Check Internet Connection: Ensure that both the computer initiating the Quick Assist session and the computer receiving assistance have a stable internet connection.
- Test Network Speed: Run a speed test to confirm adequate bandwidth for Quick Assist’s operation.
- Restart Router/Modem: Restarting your network equipment can often resolve temporary connectivity issues.
2. Review Firewall Settings:
- Disable Windows Firewall Temporarily: Temporarily disable the Windows Firewall on both computers to determine if it’s interfering with Quick Assist.
- Add Quick Assist to Firewall Exceptions: If disabling the firewall isn’t feasible, add Quick Assist to the list of exceptions in the Windows Firewall settings, allowing it to operate freely.
3. Check User Account Permissions:
- Ensure Administrative Privileges: Verify that both the user initiating the Quick Assist session and the user receiving assistance have administrative privileges on their respective computers.
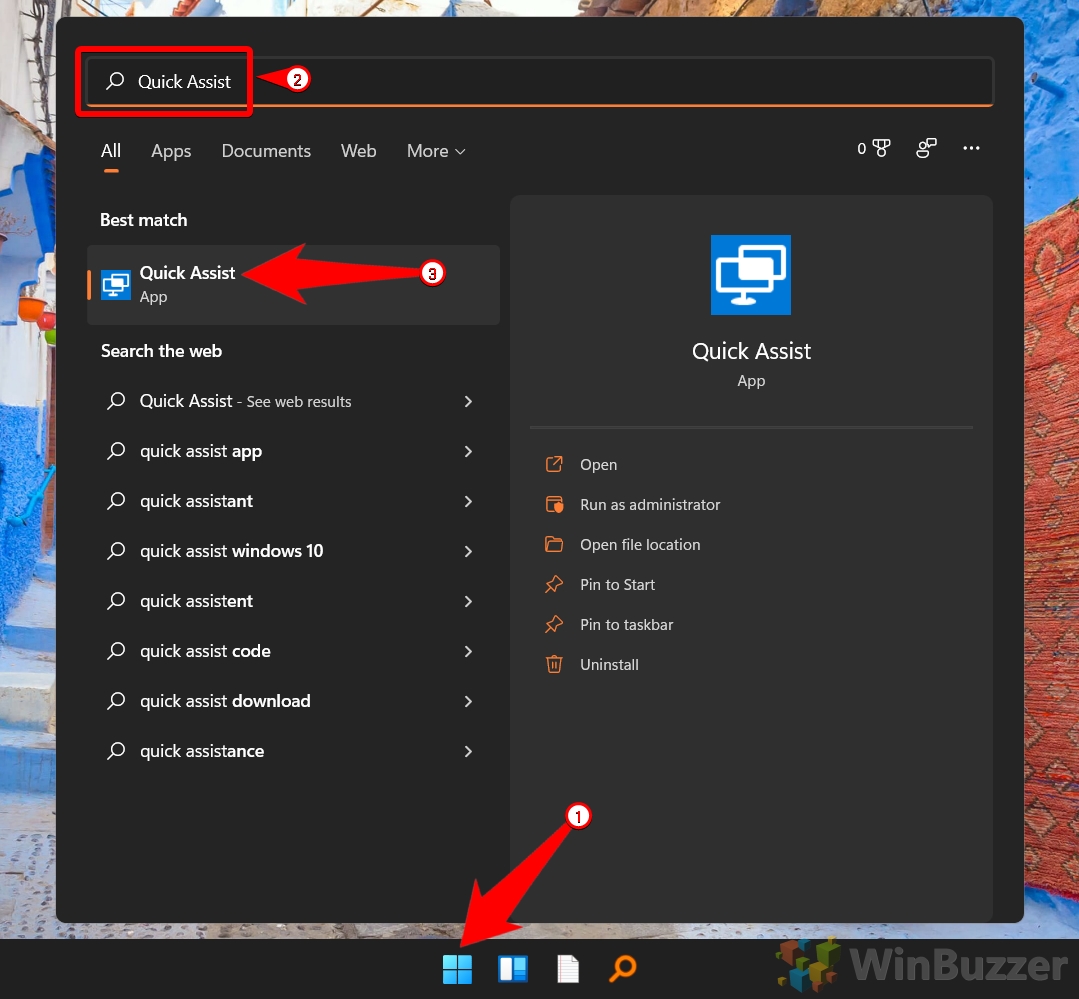
- Run Quick Assist as Administrator: If necessary, right-click the Quick Assist application and select "Run as administrator" to ensure sufficient permissions for the connection.
4. Update Drivers and Software:
- Update Network Drivers: Ensure that both computers have the latest network drivers installed.
- Update Windows Operating System: Keep both computers updated with the latest Windows 11 updates to address potential compatibility issues.
5. Troubleshoot System Errors:
- Run System File Checker (SFC): Use the SFC tool to scan for and repair corrupted system files that might be interfering with Quick Assist.
- Restart the Computer: Restarting the computer can often resolve temporary system errors that might be causing Quick Assist issues.
6. Consider Alternative Solutions:
- Use Remote Desktop: If Quick Assist continues to malfunction, consider using the built-in Remote Desktop feature in Windows 11.
- Utilize Third-Party Remote Access Software: Explore third-party remote access software solutions like TeamViewer or AnyDesk, which offer similar functionalities to Quick Assist.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions
Q1: Why can’t I connect to another computer using Quick Assist?
- A: Several factors can prevent a Quick Assist connection. Check your network connection, firewall settings, user account permissions, and ensure that both computers are running compatible versions of Windows 11.
Q2: I’m getting an error message when trying to connect. What does it mean?
- A: Error messages can provide valuable clues to the cause of the issue. Carefully review the error message and search for relevant troubleshooting guides online.
Q3: How do I know if Quick Assist is working properly?
- A: To test Quick Assist, attempt to connect to another computer on the same network. If the connection is successful, Quick Assist is functioning correctly.
Q4: Can I use Quick Assist to access a computer remotely over the internet?
- A: While Quick Assist primarily focuses on local network connections, it can be configured to work over the internet with some additional steps.
Q5: Is there a way to improve Quick Assist’s performance?
- A: Ensure a strong internet connection, minimize background processes on both computers, and consider using a wired connection for optimal performance.
Tips for Utilizing Quick Assist Effectively
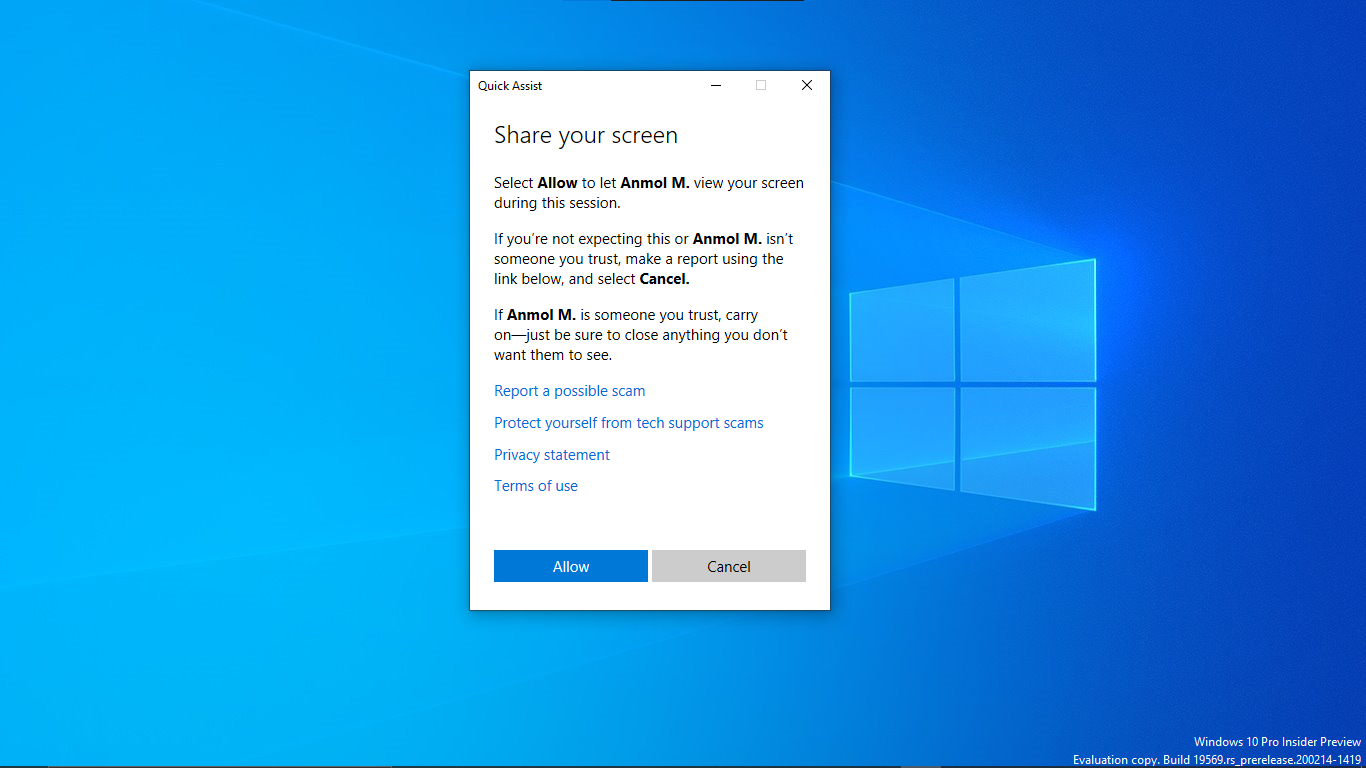
- Grant Necessary Permissions: Before initiating a Quick Assist session, ensure that the user receiving assistance grants the necessary permissions to the remote user.
- Communicate Clearly: Provide clear instructions and explanations during the Quick Assist session to ensure the user receiving assistance understands the process.
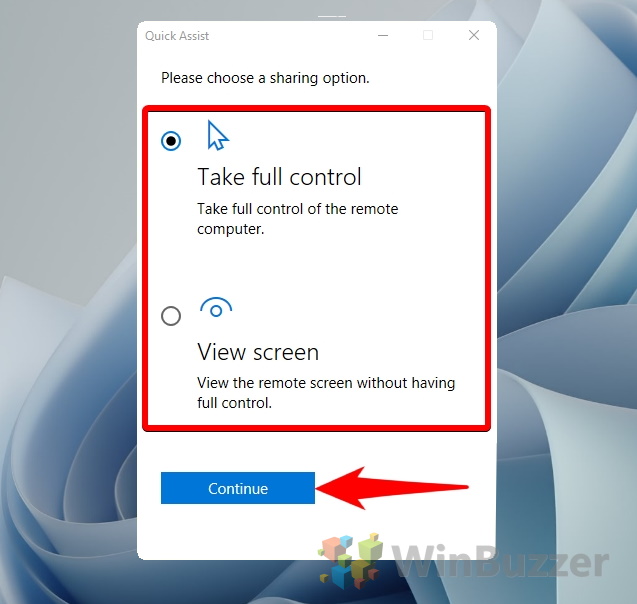
- Use Screen Sharing: Utilize the screen sharing feature to demonstrate procedures and provide visual guidance during the troubleshooting process.
- Explore Additional Features: Familiarize yourself with the various features offered by Quick Assist, such as file sharing and remote control, to maximize its capabilities.
Conclusion
Windows 11’s Quick Assist feature offers a powerful solution for remote assistance, enabling users to connect, collaborate, and troubleshoot issues efficiently. While Quick Assist can occasionally encounter issues, understanding the common causes of malfunctions and implementing the troubleshooting steps outlined in this guide can effectively restore its functionality. By addressing network connectivity problems, firewall restrictions, user account permissions, and system errors, users can unlock the full potential of Quick Assist, leveraging its benefits for seamless remote assistance and collaboration.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unlocking the Potential of Remote Assistance: Troubleshooting Windows 11 Quick Assist Issues. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!