Understanding FAT32 File System and its Compatibility with Windows 11
Related Articles: Understanding FAT32 File System and its Compatibility with Windows 11
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding FAT32 File System and its Compatibility with Windows 11. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding FAT32 File System and its Compatibility with Windows 11
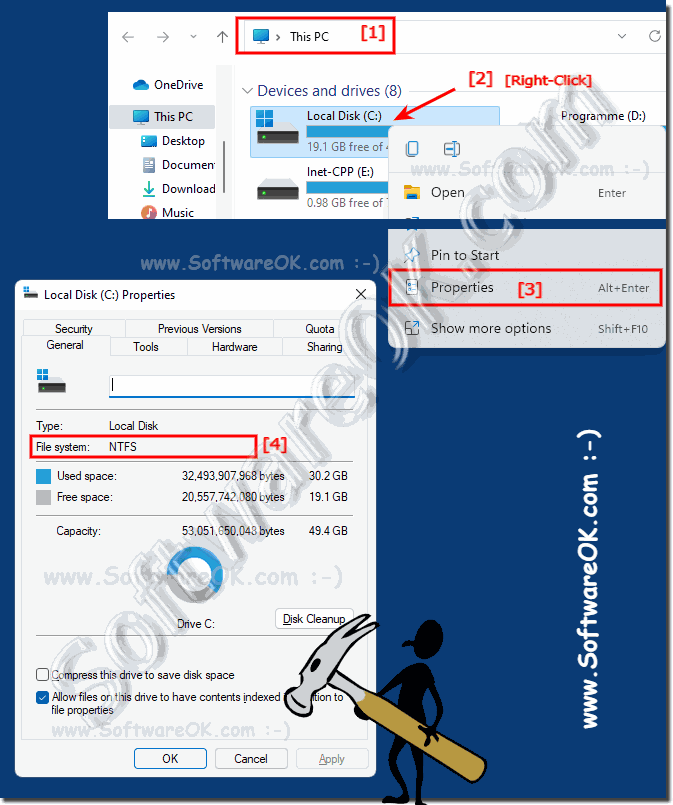
The ability of Windows 11 to read and write data on FAT32 formatted USB drives is a crucial aspect of its functionality, facilitating seamless data transfer and device compatibility across various operating systems and devices. To understand this capability fully, it’s essential to delve into the fundamentals of the FAT32 file system and its relevance in the contemporary technological landscape.
FAT32: A Legacy File System with Modern Applications
FAT32, an acronym for File Allocation Table 32, is a file system that has been a mainstay in the world of personal computing for decades. Developed by Microsoft, it was first introduced with Windows 95 and has since become a ubiquitous standard for formatting storage devices, particularly USB drives, SD cards, and external hard drives.
The FAT32 file system’s popularity stems from its simplicity and compatibility. It is a relatively lightweight file system, requiring minimal overhead, making it efficient for smaller storage devices. Moreover, its cross-platform compatibility, allowing data exchange between Windows, macOS, Linux, and various embedded systems, has cemented its position as a reliable file system for data sharing.
Windows 11 and FAT32: A Harmonious Partnership
Windows 11, the latest iteration of Microsoft’s flagship operating system, seamlessly integrates with the FAT32 file system, ensuring smooth data transfer and device interaction. This compatibility is crucial for various reasons:
-
Legacy Device Support: Many older devices, particularly those with limited storage capacity, use FAT32 for formatting. Windows 11’s ability to read and write to these devices ensures backward compatibility, allowing users to access data stored on older devices without encountering issues.
-
Cross-Platform Data Exchange: FAT32’s cross-platform nature enables easy sharing of files between Windows 11 and other operating systems. This is particularly important for users who work with multiple devices or need to share files with individuals using different platforms.
-
Universal Compatibility: FAT32 is widely recognized and supported by various devices, including cameras, smartphones, gaming consoles, and multimedia players. This universal compatibility makes it a convenient choice for transferring files between different devices.
-
Simple File Management: FAT32’s straightforward structure makes it easy to manage files and folders, even for users unfamiliar with complex file systems. This simplicity contributes to a user-friendly experience, particularly when working with USB drives.
Advantages of Using FAT32 with Windows 11
While newer file systems like NTFS offer advanced features and larger file size support, FAT32 remains a valuable option for specific scenarios due to its inherent advantages:
-
Broad Compatibility: FAT32’s wide compatibility across various operating systems and devices ensures seamless data transfer and device interaction.
-
Universal Support: FAT32 is supported by almost all devices, making it the ideal file system for transferring files between different platforms.
-
Lightweight and Efficient: FAT32 requires minimal overhead, making it efficient for smaller storage devices like USB drives and SD cards.
-
Simple File Management: FAT32’s straightforward structure simplifies file management, making it user-friendly for all levels of computer experience.
Limitations of FAT32
While FAT32 offers numerous advantages, it also has certain limitations:
-
Limited File Size Support: FAT32 has a maximum file size limit of 4GB, which can be problematic for transferring large files like videos or high-resolution images.
-
Limited Partition Size: FAT32 partitions are limited to a maximum size of 32GB, making it unsuitable for formatting large storage devices like external hard drives.
-
Lack of Advanced Features: FAT32 lacks advanced features found in newer file systems like NTFS, such as file encryption, permissions, and journaling.
Alternatives to FAT32
For scenarios where FAT32’s limitations become a bottleneck, alternative file systems like NTFS (New Technology File System) and exFAT (Extended File Allocation Table) offer more features and flexibility:
-
NTFS: This file system, developed by Microsoft, provides advanced features like file encryption, permissions, and larger file size support. However, it is not as universally compatible as FAT32.
-
exFAT: This file system offers improved file size and partition size limits compared to FAT32, making it suitable for larger storage devices. It also boasts good compatibility with various operating systems.
Choosing the Right File System
The choice of file system depends on the specific use case and device:
-
For smaller storage devices like USB drives and SD cards: FAT32 is an excellent choice due to its broad compatibility and simplicity.
-
For larger storage devices like external hard drives: NTFS or exFAT are preferable, offering larger file size and partition size support, and advanced features.
-
For cross-platform data sharing: FAT32 remains a reliable option due to its wide compatibility with various operating systems.
FAQs
Q: Can I format a USB drive to FAT32 in Windows 11?
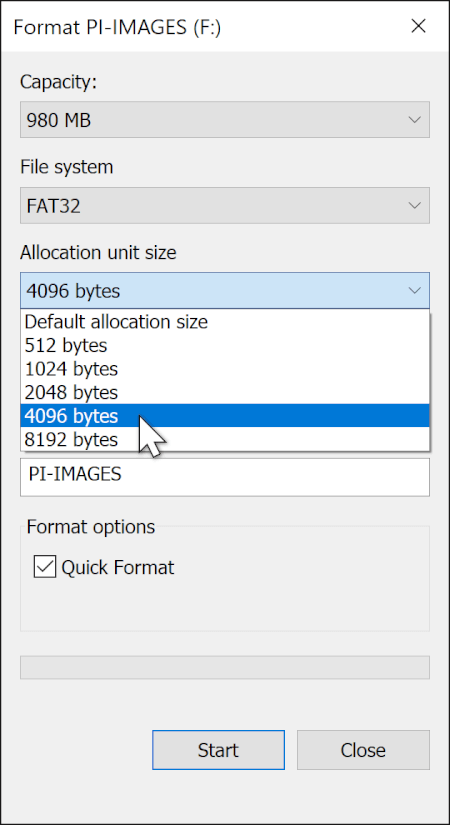
A: Yes, Windows 11 allows you to format USB drives to FAT32. To do so, open File Explorer, right-click on the USB drive, select "Format," and choose FAT32 from the file system dropdown menu.
Q: What is the maximum file size I can store on a FAT32 formatted USB drive?
A: The maximum file size limit for FAT32 is 4GB. This means you cannot store files larger than 4GB on a FAT32 formatted drive.
Q: Can I access data on a FAT32 formatted USB drive from other operating systems?
A: Yes, FAT32 is compatible with various operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. This ensures that you can access data stored on a FAT32 formatted USB drive from different devices.
Q: Is FAT32 still relevant in the age of newer file systems?
A: FAT32 remains relevant for specific scenarios, particularly for smaller storage devices and cross-platform data sharing. Its simplicity and wide compatibility make it a valuable option for many users.
Tips
-
Always back up important data before formatting a USB drive.
-
Consider using a file system like NTFS or exFAT for larger storage devices and larger files.
-
Ensure that the device you are transferring files to supports the file system used on the USB drive.
Conclusion
Windows 11’s ability to read and write data on FAT32 formatted USB drives is a testament to its commitment to backward compatibility and cross-platform interoperability. While newer file systems like NTFS and exFAT offer advanced features and greater flexibility, FAT32 remains a valuable option for specific scenarios, particularly for smaller storage devices and cross-platform data sharing. Understanding the strengths and limitations of FAT32 allows users to make informed decisions regarding file system selection, ensuring optimal data transfer and device compatibility in their digital workflows.
![How to Format HDD/External Hard Drive to FAT32 in Windows 11/10 [2024 Tutorial] - EaseUS](https://www.easeus.com/images/en/screenshot/partition-manager/format-external-hard-drive-to-fat32-theme.png)

![[4+] Format SD Card FAT32 in Windows 11 with Free Software](https://www.resize-c.com/img/howto/format-sd-card-fat32.jpg)
![[4+] Format SD Card FAT32 in Windows 11 with Free Software](https://www.resize-c.com/img/howto/format-fat32-windows-dispart.gif)
![6 Ways to Format USB to FAT32 on Windows 10/11 [Full Guide]](https://images.anyrecover.com/anyrecoveren/assets/article/format-a-usb-drive-in-fat32.png)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding FAT32 File System and its Compatibility with Windows 11. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!