Understanding and Resolving Windows 11 Local Security Authority (LSA) Issues
Related Articles: Understanding and Resolving Windows 11 Local Security Authority (LSA) Issues
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Resolving Windows 11 Local Security Authority (LSA) Issues. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding and Resolving Windows 11 Local Security Authority (LSA) Issues
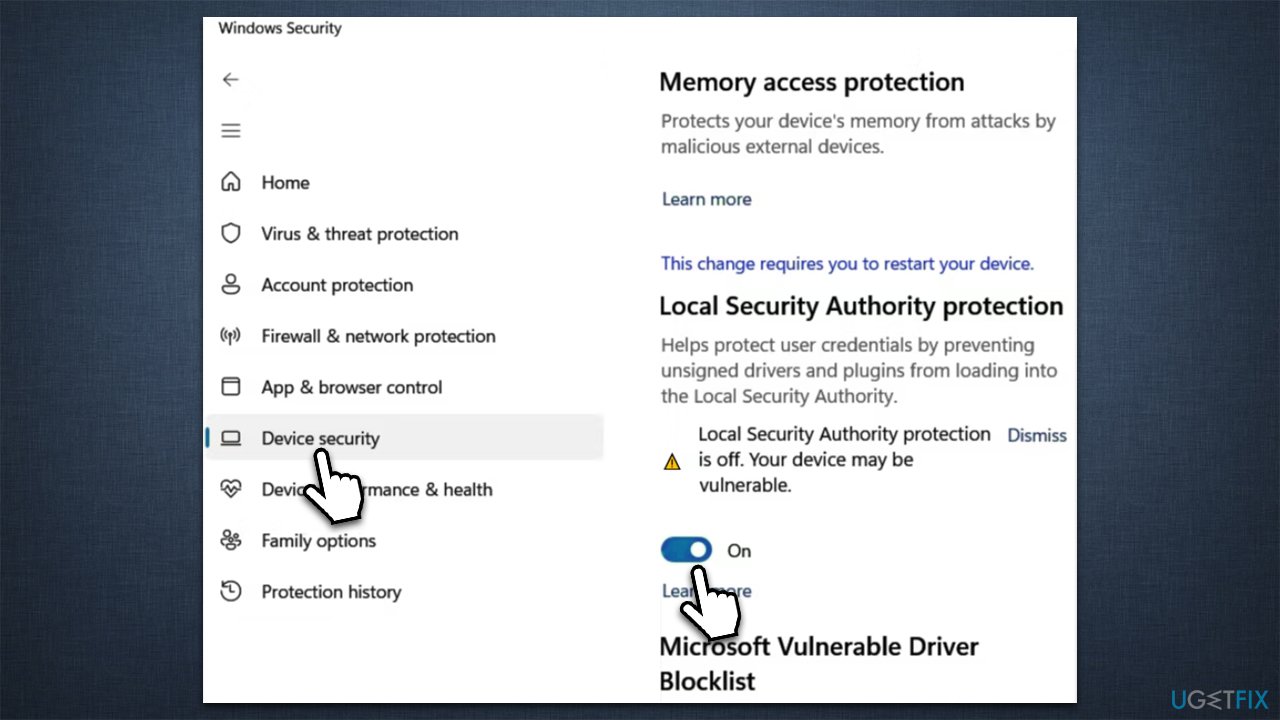
The Local Security Authority (LSA) is a critical component of the Windows operating system, responsible for managing security policies, authentication, and authorization. When the LSA fails to function properly, it can lead to various security vulnerabilities and system instability, making it crucial to address these issues promptly. This article explores the common causes of LSA failure in Windows 11, provides troubleshooting steps, and offers valuable insights into resolving this critical security concern.
Understanding the Importance of the Local Security Authority
The LSA plays a pivotal role in securing your Windows 11 system. Its primary functions include:
- Authentication: Verifying user credentials during login, ensuring only authorized individuals can access the system.
- Authorization: Enforcing access control policies, granting or denying permissions to specific users or groups based on their roles and privileges.
- Security Policy Management: Managing and enforcing security settings, including password complexity, account lockout policies, and auditing configurations.
- Credential Management: Storing and protecting user credentials, such as passwords and security tokens, to ensure secure access to resources.
- Auditing and Logging: Tracking security-related events, providing a detailed record of user actions and system activities for security analysis and incident response.
Common Causes of LSA Failure in Windows 11
Several factors can contribute to LSA failure in Windows 11, including:
- Corrupted System Files: Damaged or corrupted system files, particularly those related to the LSA, can lead to malfunctions.
- Conflicting Software: Incompatible or outdated software applications can interfere with the LSA’s functionality, causing conflicts and errors.
- Malware Infection: Malicious software can compromise the LSA, potentially disabling its security features or manipulating its operations.
- Hardware Issues: Faulty hardware components, including storage drives or memory, can also disrupt the LSA’s operation.
- Incorrect System Configuration: Improperly configured security settings or policies can lead to LSA failure, resulting in unexpected behavior or security breaches.
- Driver Issues: Outdated or incompatible device drivers can cause conflicts with the LSA, impacting its performance and stability.
- Power Issues: Sudden power outages or unstable power supplies can lead to data corruption and LSA malfunction.
Troubleshooting LSA Failure in Windows 11
Addressing LSA issues requires a systematic approach, involving troubleshooting steps to identify and resolve the underlying cause. Here’s a comprehensive guide:
1. Check for System File Corruption:
- Run the System File Checker (SFC) tool by typing "sfc /scannow" in the Command Prompt (run as administrator). This tool scans for and repairs corrupted system files.
2. Identify and Resolve Software Conflicts:
- Uninstall recently installed software that might be causing conflicts.
- Consider using a clean boot to isolate the issue and identify conflicting software.
3. Scan for Malware:
- Run a full system scan with a reputable antivirus program to detect and remove any malicious software that might be affecting the LSA.
4. Verify Hardware Functionality:
- Run hardware diagnostics to check for any faulty components, especially storage drives and memory modules.
- Consider replacing faulty components if necessary.
5. Review System Configuration:
- Ensure security settings and policies are appropriately configured, avoiding overly restrictive or conflicting configurations.
- Check for any recent changes to security settings and revert them if necessary.
6. Update Device Drivers:
- Update device drivers to the latest versions, ensuring compatibility and stability.
- Consider using the manufacturer’s website for the most up-to-date drivers.
7. Ensure Stable Power Supply:
- Use a reliable power source with surge protection to prevent power fluctuations and data corruption.
- Consider using a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) for added protection against power outages.
8. Perform a System Restore:
- If the issue persists, consider restoring your system to a previous restore point before the problem occurred.
- This can help revert any changes that might have caused the LSA failure.
9. Reinstall Windows 11:
- As a last resort, consider reinstalling Windows 11 if the above troubleshooting steps fail to resolve the issue.
- Ensure you have a backup of your important data before proceeding with a clean installation.
10. Seek Professional Help:
- If you’re unable to resolve the issue independently, consider seeking assistance from a qualified IT professional who can diagnose and repair the problem effectively.
FAQs:
Q: What are the symptoms of LSA failure in Windows 11?
A: Common symptoms include:
- Failure to log in to Windows 11
- System crashes or freezes
- Error messages related to security or authentication
- Slow system performance
- Unexpected program behavior
- Inability to access certain files or folders
Q: Can I fix LSA failure myself?
A: Yes, many LSA issues can be resolved through troubleshooting steps outlined above. However, if the problem persists or involves complex system configurations, seeking professional help is recommended.
Q: What happens if I ignore LSA issues?
A: Ignoring LSA issues can lead to security vulnerabilities, allowing unauthorized access to your system and data. It can also cause system instability and data loss.
Q: Can I prevent LSA failure in the future?
A: You can minimize the risk of LSA failure by:
- Keeping your system updated with the latest security patches and updates.
- Using a reputable antivirus program and regularly scanning for malware.
- Maintaining a stable power supply with surge protection.
- Regularly backing up your important data.
Tips for Preventing LSA Failure:
- Regularly Update Windows: Install the latest security updates and patches to address vulnerabilities and improve system stability.
- Use a Strong Antivirus: Employ a reputable antivirus program and keep it updated to detect and remove malware that could affect the LSA.
- Maintain Secure Passwords: Use strong, unique passwords for all your accounts and avoid using the same password for multiple accounts.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: Implement two-factor authentication for critical accounts to enhance security and prevent unauthorized access.
- Regularly Back Up Data: Create regular backups of your important data to protect against data loss in case of system failures or security breaches.
Conclusion:
The Local Security Authority (LSA) is a crucial component of Windows 11, responsible for safeguarding your system and data. While LSA issues can be challenging to resolve, understanding the common causes and troubleshooting steps can help you address these problems effectively. By following the tips and guidelines outlined in this article, you can minimize the risk of LSA failure and maintain a secure and stable Windows 11 environment. Remember, if you’re unable to resolve the issue independently, seeking professional assistance from a qualified IT professional is always a wise decision.
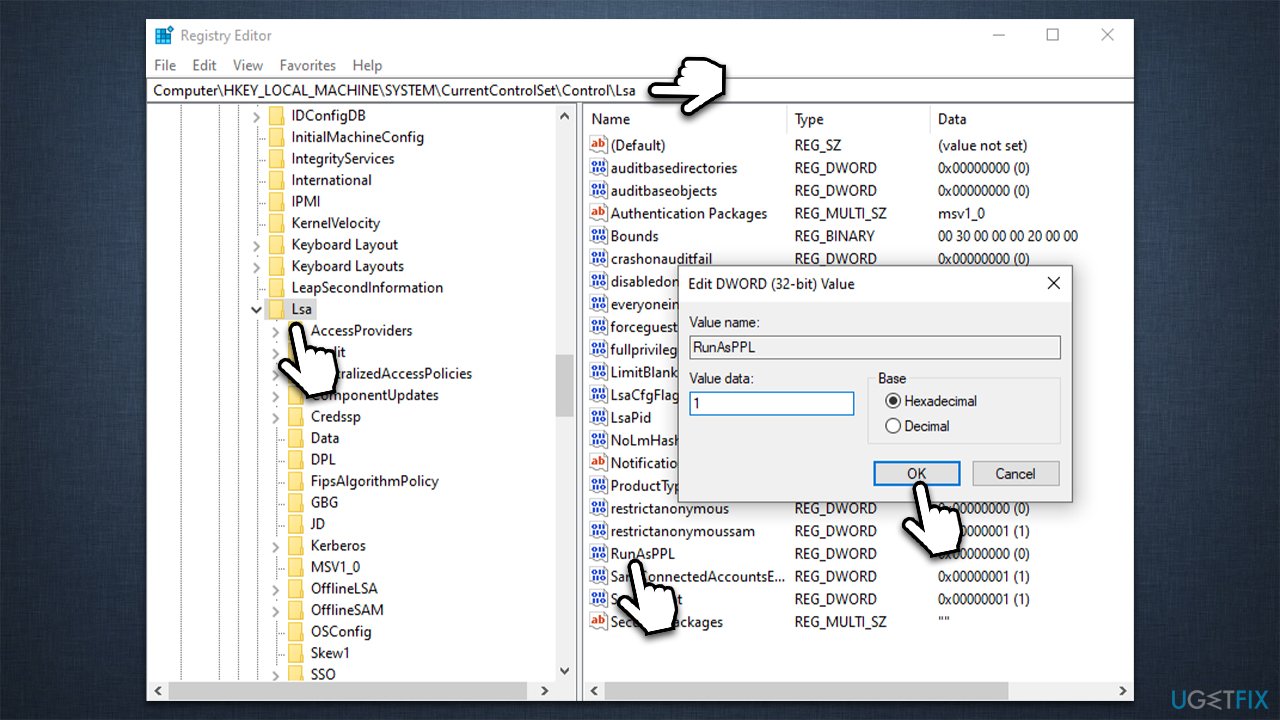



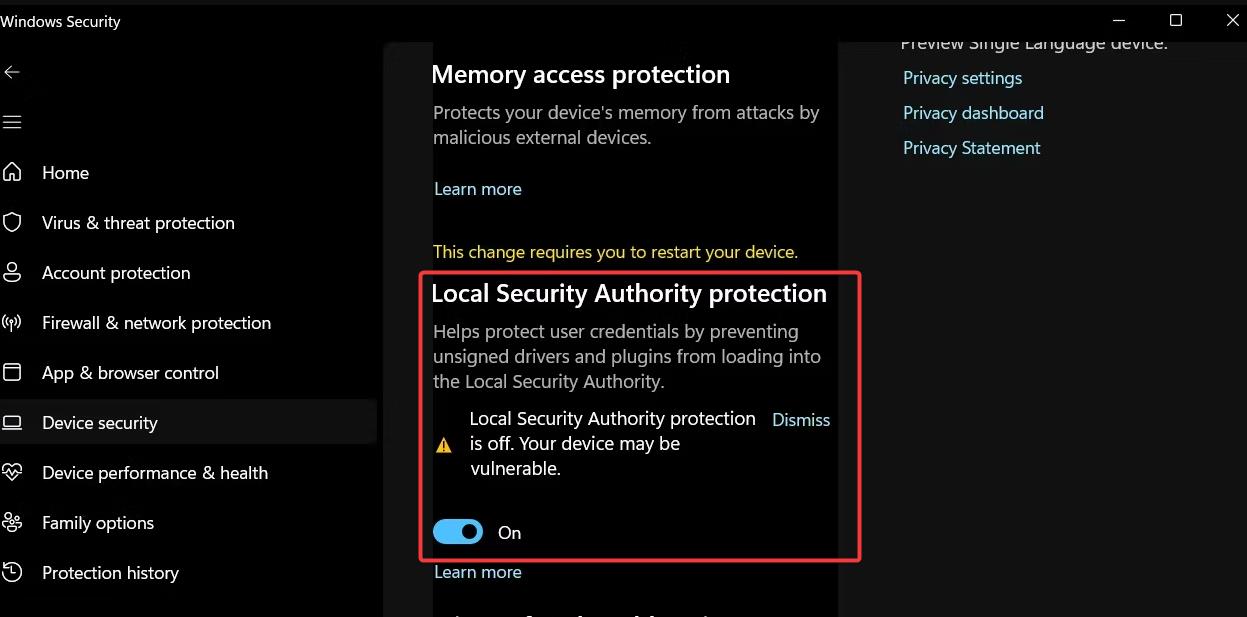
![How to Fix Local Security Authority Process high CPU Windows 11 [Steps] – Techs & Gizmos](https://techsgizmo.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Local-Security-Authority-process-high-CPU-Windows-11_.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Resolving Windows 11 Local Security Authority (LSA) Issues. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!