Understanding and Addressing Performance Issues in Windows 11
Related Articles: Understanding and Addressing Performance Issues in Windows 11
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding and Addressing Performance Issues in Windows 11. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding and Addressing Performance Issues in Windows 11

Windows 11, while a visually appealing and feature-rich operating system, can sometimes exhibit performance issues. This can manifest in various ways, such as slow startup times, sluggish application loading, lagging during gameplay, or general system unresponsiveness. Understanding the root causes of these performance hiccups is crucial for effectively addressing them and restoring optimal system performance.
Common Culprits Behind Performance Degradation
Several factors can contribute to Windows 11 running slower than expected. Identifying the specific culprit is the first step towards resolving the issue. Some of the most common causes include:
1. Insufficient Hardware Resources:
- Limited RAM: Insufficient RAM (Random Access Memory) can lead to system slowdowns as Windows struggles to manage multiple running applications and processes. This is particularly noticeable when multitasking or running resource-intensive programs.
- Storage Bottleneck: A slow hard disk drive (HDD) or a nearly full solid-state drive (SSD) can significantly impact overall system performance. The operating system and applications need to access data frequently, and a slow storage device can create a bottleneck, causing delays.
- Outdated or Underpowered CPU: The central processing unit (CPU) is the brain of the computer, and an outdated or underpowered CPU can struggle to keep up with the demands of modern software and applications. This can lead to noticeable lag, especially during tasks that require significant processing power.
- Outdated Graphics Card: Graphics cards play a vital role in visual performance, particularly in games and other graphics-intensive applications. An outdated or underpowered graphics card can result in choppy frame rates and stuttering.
2. Software-Related Factors:
- Background Processes: Numerous applications and services run in the background, consuming system resources. Some of these processes may be unnecessary or resource-intensive, leading to slowdowns.
- Startup Programs: Many applications automatically launch at system startup, adding to the initial boot time and consuming resources.
- Malware and Viruses: Malicious software can significantly impact system performance by consuming resources, interfering with normal operations, or even corrupting files.
- Outdated Drivers: Drivers are software programs that allow your computer to communicate with hardware devices. Outdated or incompatible drivers can lead to various performance issues.
- Bloatware: Pre-installed software that comes bundled with new computers, often referred to as bloatware, can consume valuable disk space and system resources.
3. System Settings and Configurations:
- Visual Effects: Windows 11 offers various visual effects that can enhance the user experience but also consume system resources. Disabling or reducing these effects can improve performance.
- Power Plan: The power plan setting can significantly impact performance. Choosing a high-performance plan can provide a boost, but it may lead to higher energy consumption.
- Indexing: Windows uses indexing to improve search speed, but this process can consume resources. Disabling indexing can improve performance, especially on older or slower machines.
4. Other Factors:
- Overheating: High temperatures can negatively affect CPU and other hardware components, leading to performance degradation.
- Dust Accumulation: Dust buildup inside the computer can hinder airflow and cause overheating, impacting performance.
Addressing Performance Issues: A Systematic Approach
Once the potential causes of slow performance have been identified, the next step is to address them systematically. Here’s a comprehensive guide:
1. Optimize Hardware:
- Upgrade RAM: If RAM is identified as a bottleneck, consider upgrading to a higher capacity.
- Upgrade Storage: Replacing an HDD with an SSD or upgrading to a larger SSD can significantly improve performance.
- Consider CPU Upgrade: If the CPU is outdated or underpowered, upgrading to a newer and more powerful model might be necessary.
- Update Graphics Card: Ensure the graphics card is up-to-date and suitable for the desired applications.
2. Manage Software:
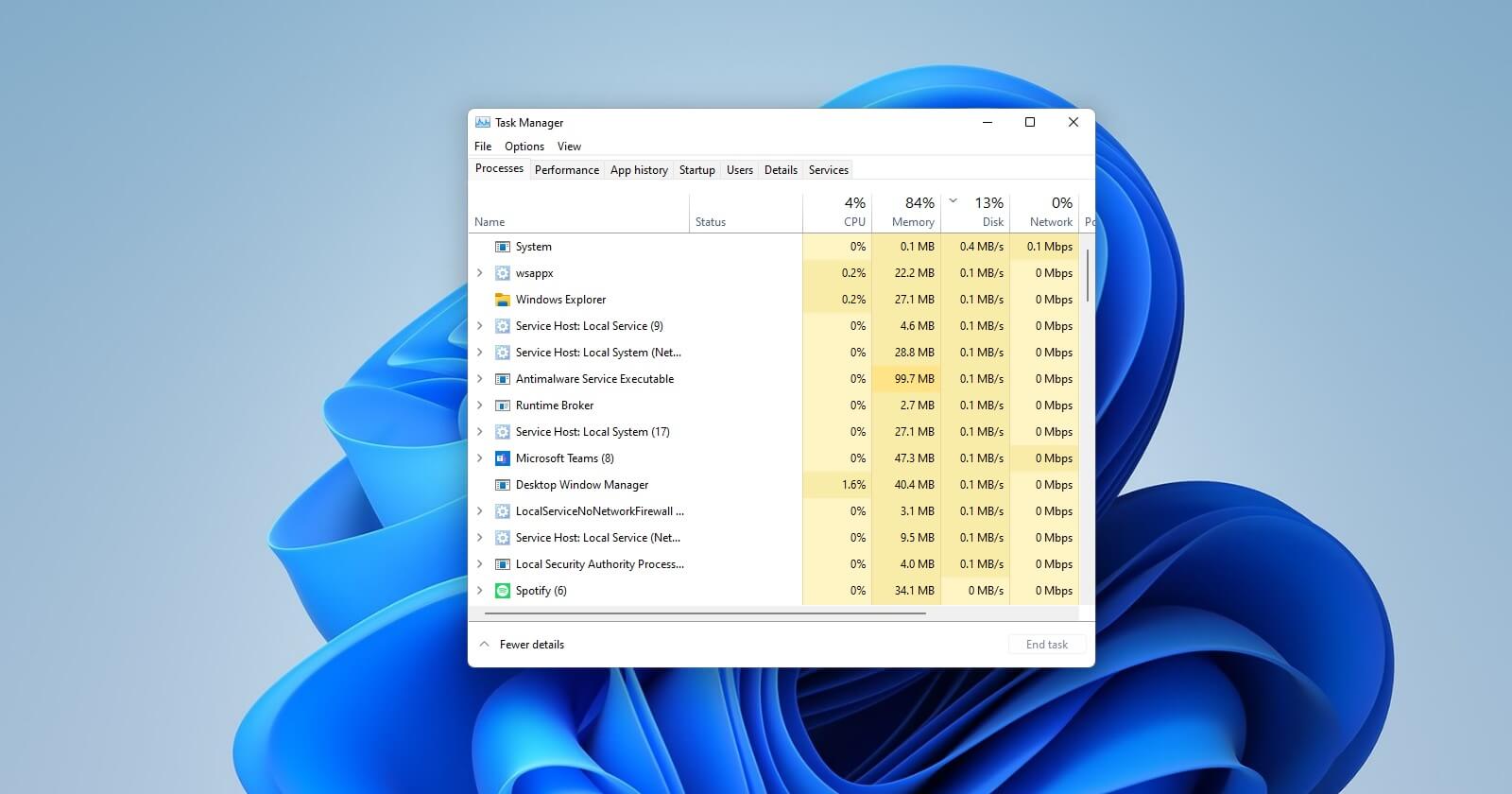
- Identify and Disable Unnecessary Background Processes: Use the Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc) to identify resource-intensive processes and disable them if they are not essential.
- Minimize Startup Programs: Use the "Startup" tab in Task Manager to disable programs that are not required to launch at startup.
- Run a Malware Scan: Regularly scan your system for malware and viruses using reputable antivirus software.
- Update Drivers: Ensure all drivers are up-to-date by checking for updates through the Device Manager (right-click on the Start menu and select "Device Manager").
- Remove Bloatware: Uninstall unnecessary pre-installed software to free up disk space and resources.
3. Fine-Tune System Settings:
- Adjust Visual Effects: Navigate to "System Settings" > "System" > "Display" and adjust the visual effects to reduce resource consumption.
- Choose a High-Performance Power Plan: Go to "Control Panel" > "Power Options" and select a high-performance plan for better performance.
- Disable Indexing: In "File Explorer," right-click on the drive you want to disable indexing for, select "Properties," and uncheck the "Allow files on this drive to be indexed" option.
4. Address Other Factors:
- Monitor and Control Temperatures: Use monitoring tools to check CPU and other component temperatures. If overheating is detected, ensure proper airflow and consider cleaning the computer’s internal components.
- Regularly Clean Your Computer: Dust buildup can significantly impact performance. Regularly clean the computer’s internal components to ensure proper airflow.
Troubleshooting Tips
- Use the Performance Monitor: The Performance Monitor (accessible through the "Performance" tab in Task Manager) provides detailed information about system resource utilization, helping identify potential bottlenecks.
- Run a System File Checker: The System File Checker (SFC) tool can scan and repair corrupted system files that may be causing performance issues. To run SFC, open Command Prompt as administrator and type "sfc /scannow."
- Run a Disk Cleanup: The Disk Cleanup tool can help free up disk space by removing unnecessary files. To access Disk Cleanup, right-click on the drive you want to clean and select "Properties."
- Consider a Fresh Install: If all else fails, a clean installation of Windows 11 might be necessary to resolve persistent performance issues. However, this should be considered as a last resort as it requires backing up all important data.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Why is my Windows 11 computer slow even though it has enough RAM?
A: While sufficient RAM is crucial for performance, other factors can contribute to slowdowns, such as a slow storage drive, outdated drivers, resource-intensive background processes, or malware infections.
Q: Can a slow internet connection affect Windows 11 performance?
A: A slow internet connection can impact the performance of online activities and applications that rely on internet connectivity. However, it should not directly affect the overall system performance.
Q: My Windows 11 computer is very slow after an update. What should I do?
A: Updates can sometimes introduce performance issues. Try restarting your computer, running a system file checker, and checking for driver updates. If the problem persists, consider rolling back to a previous version of Windows.
Q: How can I prevent Windows 11 from getting slow over time?
A: Regularly maintain your system by running disk cleanup, managing background processes, updating drivers, and performing a malware scan. Additionally, consider upgrading your hardware if needed.
Conclusion
Performance issues in Windows 11 can be frustrating, but by understanding the common causes and following a systematic troubleshooting approach, you can identify and address these issues effectively. Regularly maintaining your system, optimizing hardware, and managing software resources are key to ensuring smooth and efficient performance. While a clean installation might be necessary in some cases, it’s important to explore all other options before resorting to such drastic measures. By taking proactive steps to address performance issues, you can enjoy a responsive and enjoyable Windows 11 experience.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding and Addressing Performance Issues in Windows 11. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!