The Guardian of Your Windows 11: Understanding the Local Security Authority
Related Articles: The Guardian of Your Windows 11: Understanding the Local Security Authority
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Guardian of Your Windows 11: Understanding the Local Security Authority. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Guardian of Your Windows 11: Understanding the Local Security Authority
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Guardian of Your Windows 11: Understanding the Local Security Authority
- 3.1 Delving into the Responsibilities of the LSA
- 3.2 The Importance of the LSA: A Foundation for Security
- 3.3 FAQs about the Local Security Authority
- 3.4 Tips for Enhancing LSA Security
- 3.5 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
The Guardian of Your Windows 11: Understanding the Local Security Authority
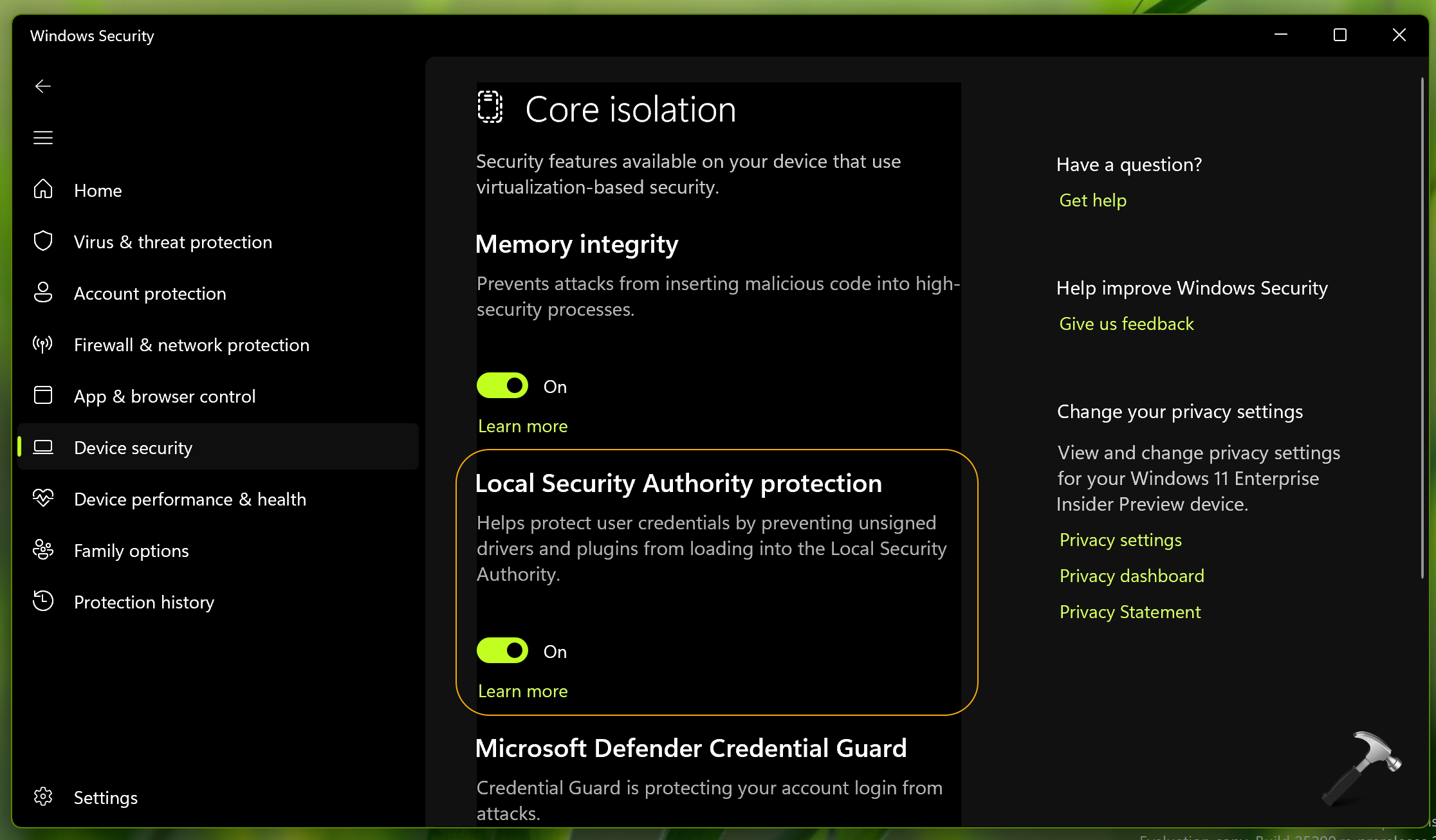
In the digital world, security is paramount. Every interaction, every file, every program, carries the potential for vulnerability. Microsoft Windows 11, like its predecessors, relies on a complex system of security measures to safeguard your data and protect your system from unauthorized access. At the heart of this intricate security framework lies the Local Security Authority (LSA).
The LSA is a fundamental component of Windows 11’s operating system, acting as a central authority for security-related functions. It plays a vital role in managing user authentication, access control, and security policies, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of your system.
Delving into the Responsibilities of the LSA
The LSA’s responsibilities extend far beyond a simple gatekeeper role. It is actively involved in a multitude of security-critical tasks:
1. Authentication and Authorization:
-
User Login: When you log in to Windows 11, the LSA verifies your credentials. It compares your provided username and password against a database of authorized users. If the credentials match, the LSA grants you access to the system, allowing you to interact with your files, applications, and other resources.
-
Access Control: The LSA governs access to system resources based on defined policies. It determines which users have permission to access specific files, folders, and programs. This granular control ensures that only authorized individuals can interact with sensitive information.
2. Security Policy Enforcement:
-
Group Policy Management: The LSA enforces the security policies defined by your system administrator or by default settings. These policies dictate various security aspects, including password complexity requirements, account lockout policies, and access restrictions.
-
Auditing and Logging: The LSA monitors system activity and logs events related to security, such as failed login attempts, file access attempts, and changes to security settings. These logs provide valuable insights into potential security breaches and help in troubleshooting security issues.
3. Secure Communication:
- Secure Channel: The LSA establishes a secure communication channel between the operating system and other applications. This channel ensures that sensitive data exchanged between applications is protected from eavesdropping and tampering.
4. Privilege Elevation:
- User Account Control (UAC): When an application requires elevated privileges, the LSA prompts the user for confirmation. This mechanism prevents malicious programs from gaining unauthorized access to system resources.
The Importance of the LSA: A Foundation for Security
The LSA is not just a component of Windows 11; it is the bedrock upon which the entire security infrastructure rests. Its importance cannot be overstated:
-
Preventing Unauthorized Access: By diligently verifying user credentials and enforcing access control policies, the LSA acts as the first line of defense against unauthorized access to your system.
-
Maintaining System Integrity: The LSA ensures that only authorized changes are made to system settings and configurations, preventing malicious tampering and maintaining the integrity of your operating system.
-
Protecting Sensitive Data: The LSA’s secure communication channels and access control mechanisms protect sensitive data from unauthorized access and disclosure, safeguarding your privacy and confidential information.
-
Facilitating Secure Collaboration: The LSA allows you to share resources with other users while maintaining control over access permissions, enabling secure collaboration and data sharing within a controlled environment.
FAQs about the Local Security Authority
1. How does the LSA protect my data from malware?
The LSA enforces access control policies, preventing malicious programs from accessing sensitive data without authorization. It also monitors system activity and logs suspicious events, helping to detect and respond to malware threats.
2. Can I configure the LSA settings myself?
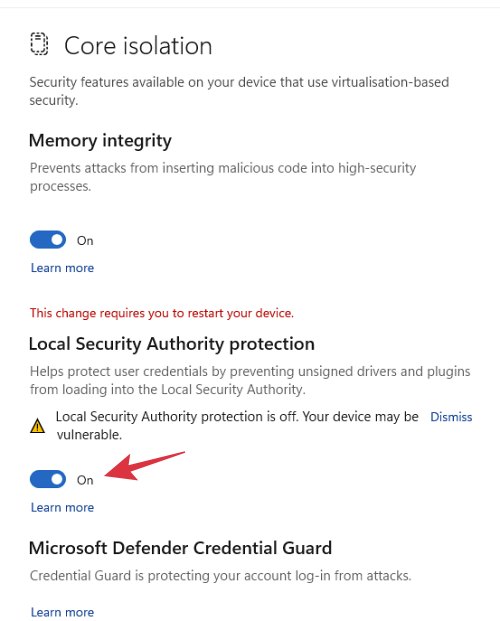
While some LSA settings can be configured through the Windows 11 user interface, advanced configurations are typically handled by system administrators using Group Policy Editor or other administrative tools.
3. What happens if the LSA fails?
A failure in the LSA can severely compromise system security, potentially leading to unauthorized access, data breaches, and system instability. It is crucial to ensure the LSA is functioning correctly and to address any issues promptly.
4. How can I ensure the LSA is working properly?
You can monitor the LSA’s health by checking the system logs for any errors or warnings related to security events. Regular security updates and system maintenance can also help prevent LSA-related issues.
Tips for Enhancing LSA Security
1. Strong Passwords: Use strong passwords that are difficult to guess and avoid reusing passwords across multiple accounts.
2. Regular Security Updates: Install all security updates promptly to patch vulnerabilities and ensure the LSA is protected against the latest threats.
3. Enable User Account Control (UAC): UAC prompts you for confirmation before applications attempt to make changes to system settings, helping to prevent unauthorized modifications.
4. Limit Administrator Privileges: Avoid running applications with administrator privileges unless absolutely necessary.
5. Monitor System Logs: Regularly review system logs for suspicious activity, including failed login attempts, unusual file access patterns, and changes to security settings.
6. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Use MFA whenever possible to add an extra layer of security to your accounts and protect your data.
7. Secure Your Network: Use strong passwords for your Wi-Fi network and keep your router firmware up to date to prevent unauthorized access to your system.
8. Be Aware of Phishing Attempts: Be cautious of suspicious emails, links, and attachments that could lead to malware infections or data theft.
9. Use Antivirus Software: Install and maintain a reputable antivirus program to protect your system from malware and other threats.
10. Back Up Your Data: Regularly back up your important data to a secure location to prevent data loss in case of system failure or security breaches.
Conclusion
The Local Security Authority is an essential component of Windows 11’s security architecture, providing a robust foundation for protecting your system and data from unauthorized access and malicious threats. By understanding the LSA’s role and implementing appropriate security measures, you can enhance your system’s security and safeguard your digital assets.
Remember, security is an ongoing process. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and take proactive steps to protect your system and your data.


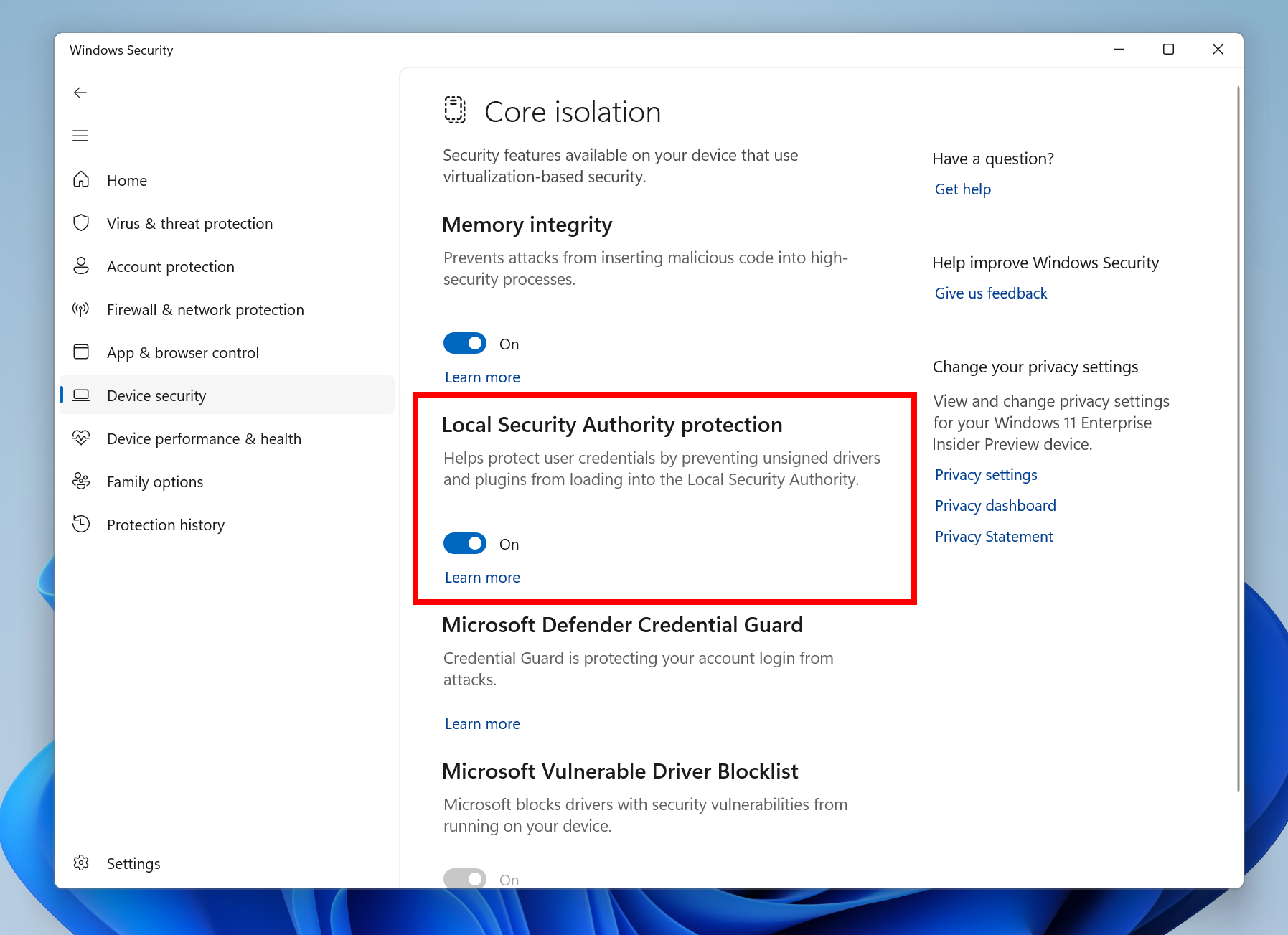

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Guardian of Your Windows 11: Understanding the Local Security Authority. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!