The Absence of Windows 11 32-bit: Understanding the Shift in Operating Systems
Related Articles: The Absence of Windows 11 32-bit: Understanding the Shift in Operating Systems
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Absence of Windows 11 32-bit: Understanding the Shift in Operating Systems. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Absence of Windows 11 32-bit: Understanding the Shift in Operating Systems

The realm of operating systems is constantly evolving, with each new iteration aiming to enhance performance, security, and user experience. Microsoft’s Windows 11, released in 2021, marked a significant shift in this evolution. While previous versions of Windows offered both 32-bit and 64-bit architectures, Windows 11 exclusively supports the latter. This decision, driven by technological advancements and the increasing limitations of 32-bit systems, has raised questions and sparked discussions within the tech community.
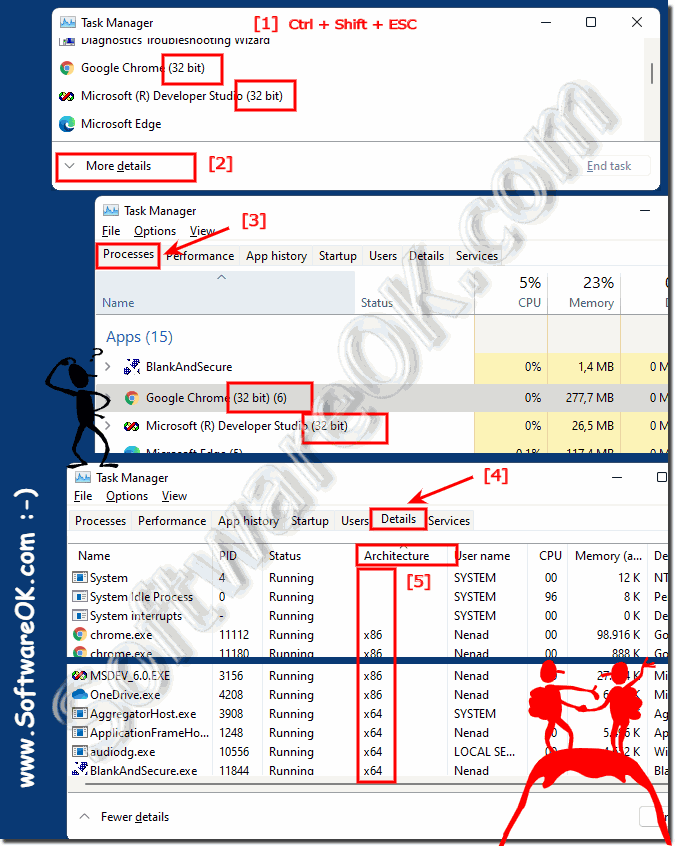
Understanding the 32-bit and 64-bit Distinction
To understand the significance of Windows 11’s exclusive 64-bit support, it is essential to grasp the fundamental difference between these two architectures.
- 32-bit architecture allows a processor to access and process data in units of 32 bits at a time. This limits the maximum amount of RAM a system can utilize to 4 GB, a constraint that becomes increasingly restrictive with modern applications demanding more resources.
- 64-bit architecture significantly expands processing capabilities, enabling the processor to handle 64 bits of data simultaneously. This translates to a dramatic increase in RAM capacity, allowing for more efficient handling of complex tasks and larger data sets.
The Rationale Behind Windows 11’s 64-bit Exclusivity
Microsoft’s decision to abandon 32-bit support for Windows 11 is a testament to the advancements in computing technology and the growing demand for greater performance and efficiency.
- Increased performance: 64-bit architecture provides a significant performance boost, enabling smoother operation of demanding applications and multitasking without compromising system responsiveness.
- Enhanced security: 64-bit systems offer enhanced security features, making them less susceptible to malware and vulnerabilities commonly found in older 32-bit environments.
- Future-proofing: By embracing 64-bit technology, Microsoft aims to future-proof Windows 11, ensuring it remains compatible with upcoming hardware and software advancements.
The Impact on Users and Legacy Systems
While the shift to 64-bit architecture brings numerous advantages, it also presents challenges for users with older systems or specific hardware requirements.
- Legacy hardware incompatibility: Some older hardware components, such as specific processors or peripherals, may not be compatible with 64-bit systems.
- Software limitations: Certain legacy software applications may not have been updated to support 64-bit architectures, rendering them unusable on Windows 11.
- Upgrade considerations: Users with 32-bit systems may need to upgrade their hardware to meet the minimum requirements for running Windows 11.
Alternatives for Users with Legacy Systems
For users with 32-bit systems who are unable or unwilling to upgrade, several alternatives exist:
- Continue using Windows 10: Windows 10 remains a viable option for users with 32-bit systems, offering a familiar environment and compatibility with legacy software.
- Consider alternative operating systems: Linux distributions, such as Ubuntu or Fedora, are known for their compatibility with a wide range of hardware and software, including 32-bit systems.
- Utilize virtualization software: Virtualization software, such as VMware or Oracle VirtualBox, allows users to create virtual machines running different operating systems, including older versions of Windows, within their existing 64-bit systems.
FAQ: Addressing Common Questions
Q: Can I still install Windows 11 on a 32-bit system?
A: No, Windows 11 does not support 32-bit systems. You cannot install it on a computer with a 32-bit processor.
Q: What are the minimum system requirements for Windows 11?
A: Windows 11 requires a 64-bit processor, at least 4 GB of RAM, and 64 GB of storage space, among other specifications.
Q: What happens to my 32-bit applications after upgrading to Windows 11?
A: 32-bit applications may not function properly on Windows 11. While some applications may have 64-bit versions available, others may not be compatible.
Q: Are there any benefits to using Windows 11 on a 64-bit system?
A: Yes, Windows 11 offers significant benefits on 64-bit systems, including improved performance, enhanced security, and access to the latest features and updates.
Tips for Users Transitioning to Windows 11
- Check system compatibility: Ensure your hardware meets the minimum requirements for Windows 11 before attempting to upgrade.
- Back up your data: Before installing Windows 11, back up all your important files and settings to prevent data loss.
- Check application compatibility: Verify that your essential applications are compatible with Windows 11 before upgrading.
- Consider a clean install: For a fresh start and optimal performance, consider performing a clean install of Windows 11 rather than upgrading from a previous version.
Conclusion
The absence of a 32-bit version of Windows 11 marks a significant shift in the evolution of operating systems. While the decision to focus exclusively on 64-bit architecture brings numerous advantages, it also presents challenges for users with legacy systems. By understanding the rationale behind this shift and exploring available alternatives, users can navigate this transition effectively, ensuring they continue to utilize the latest technology while maintaining compatibility with their existing hardware and software.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Absence of Windows 11 32-bit: Understanding the Shift in Operating Systems. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!