Navigating the Compatibility Landscape: Why Windows 11 May Not Be Ideal for Older PCs
Related Articles: Navigating the Compatibility Landscape: Why Windows 11 May Not Be Ideal for Older PCs
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Navigating the Compatibility Landscape: Why Windows 11 May Not Be Ideal for Older PCs. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating the Compatibility Landscape: Why Windows 11 May Not Be Ideal for Older PCs
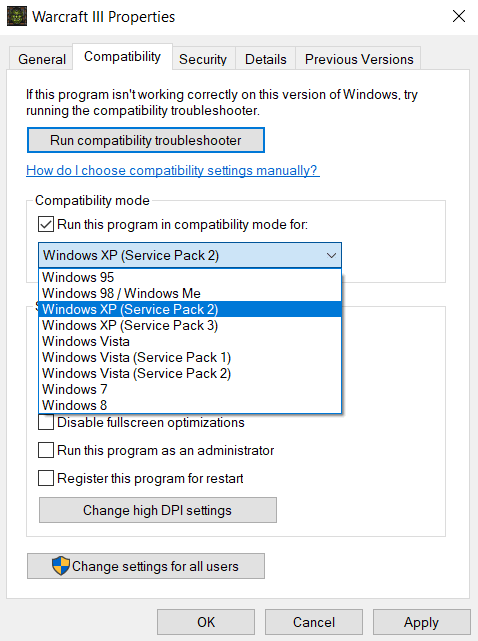
The release of Windows 11 brought with it a wave of excitement and anticipation, promising a sleek new user interface and enhanced features. However, alongside the fanfare, a crucial aspect emerged: compatibility. Microsoft, in its official documentation, explicitly outlined that Windows 11 is not recommended for older PCs, a statement that has sparked numerous discussions and raised concerns for users with legacy systems. This article delves into the reasons behind this recommendation, exploring the technical factors that necessitate this cautious approach and offering guidance for users navigating this compatibility landscape.
The Technical Landscape: A Deep Dive into Compatibility Challenges
Windows 11, in its quest for performance optimization and security enhancements, introduced a set of stringent hardware requirements. These requirements, while designed to deliver a seamless and efficient user experience, pose a significant challenge for older PCs, often lacking the necessary specifications.
1. TPM 2.0: A Security Foundation
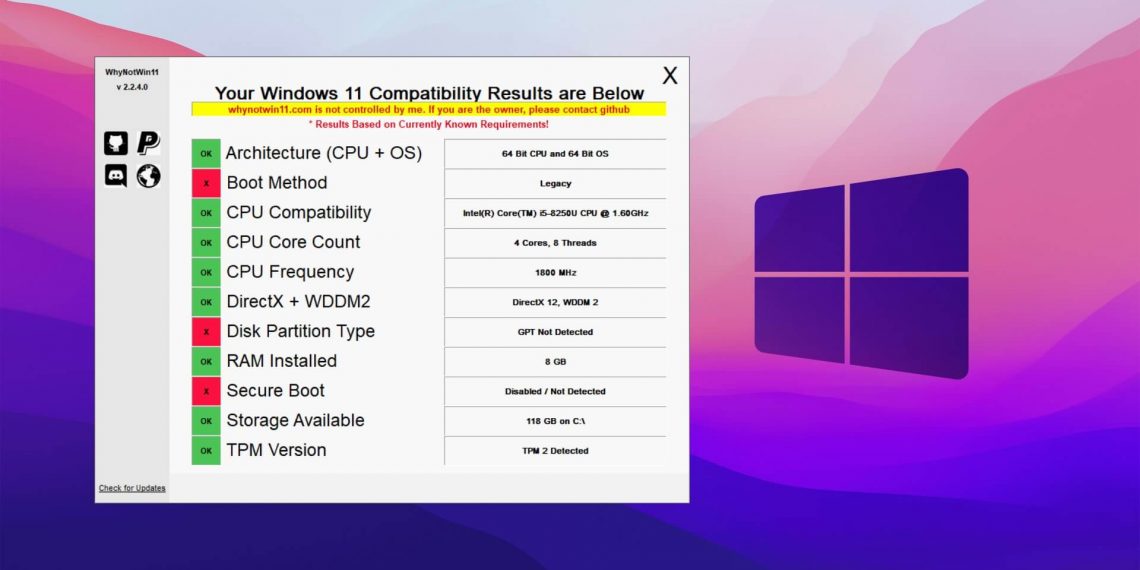
At the forefront of these requirements is the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0, a security chip embedded in the motherboard. This chip plays a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive data and protecting against malicious attacks. While newer PCs are typically equipped with TPM 2.0, older systems often lack this crucial component. The absence of TPM 2.0 restricts access to Windows 11, as it is a fundamental security feature that Microsoft deems essential for its operating system.
2. Secure Boot: Enforcing System Integrity
Another key requirement is Secure Boot, a security protocol that ensures only authorized software can load during startup. Secure Boot prevents malware from compromising the system before the operating system even loads, bolstering overall security. Older PCs, particularly those manufactured before 2016, might not have Secure Boot enabled, presenting a barrier to Windows 11 installation.
3. Processor Compatibility: The Heart of Performance
Windows 11 mandates a specific processor generation, requiring at least an 8th generation Intel Core processor or an AMD Ryzen 2000 series processor. These processors, compared to older generations, offer significantly improved performance and efficiency, contributing to the smooth operation of Windows 11. Older PCs, equipped with older processors, may struggle to meet these demands, potentially leading to sluggish performance and system instability.
4. RAM Requirements: Fueling Efficiency
Windows 11 recommends a minimum of 4GB of RAM, a requirement that ensures smooth multitasking and efficient application performance. Older PCs often come with lower RAM configurations, which can lead to performance bottlenecks and system lag when running Windows 11. The increased memory demands of Windows 11 necessitate sufficient RAM for optimal performance.
5. Storage Capacity: Ample Space for Modern Applications
Windows 11 requires a minimum of 64GB of storage space, a requirement driven by the increasing size of modern applications and operating system files. Older PCs, with limited storage capacity, may find themselves running out of space quickly, hindering the installation and smooth operation of Windows 11.
The Implications: Understanding the Potential Downsides
While Windows 11 offers a plethora of benefits, its compatibility limitations with older PCs necessitate careful consideration. Forcing Windows 11 onto an incompatible system can lead to a range of issues, impacting both user experience and system stability.
1. Performance Degradation: A Slow and Frustrating Experience
Older PCs, lacking the necessary hardware specifications, may experience significant performance degradation when running Windows 11. This can manifest as sluggish application launch times, slow system responsiveness, and frequent freezes, making the user experience frustrating and inefficient.
2. System Instability: Frequent Crashes and Errors
The lack of compatibility can lead to system instability, characterized by frequent crashes, error messages, and unexpected shutdowns. These issues can disrupt workflow, compromise data, and ultimately render the PC unusable.
3. Security Vulnerabilities: Compromised Data and System Integrity
The absence of TPM 2.0 and Secure Boot on older PCs can leave the system vulnerable to security threats. Malware and other malicious attacks can exploit these vulnerabilities, compromising user data and system integrity.
4. Software Compatibility: Limited Functionality and Functionality
Older PCs may encounter compatibility issues with certain software and applications designed for Windows 11. This can limit functionality, prevent the use of essential programs, and hinder overall productivity.
Navigating the Options: Making Informed Choices
Understanding the compatibility landscape empowers users to make informed decisions about their upgrade options.
1. Staying with Windows 10: A Stable and Familiar Environment
For older PCs, sticking with Windows 10 remains a viable option. Windows 10 continues to receive security updates and is a stable and familiar environment for users. This option offers a balance between stability and functionality for older systems.
2. Upgrading Hardware: Investing in a Smoother Experience
If a user desires the benefits of Windows 11, upgrading their hardware components, such as the processor, RAM, and storage, can improve compatibility and enhance performance. This option involves a financial investment, but it can unlock the full potential of Windows 11.
3. Exploring Alternative Operating Systems: Expanding the Horizon
For users seeking a more lightweight and resource-efficient operating system, exploring alternatives like Linux distributions or Chrome OS can be a viable solution. These operating systems are often designed for resource-constrained systems and offer a range of customization options.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries about Compatibility
Q: Can I still install Windows 11 on my older PC?
A: While technically possible through workarounds, Microsoft explicitly discourages installing Windows 11 on older PCs due to potential compatibility issues and security risks.
Q: What are the benefits of staying with Windows 10?
A: Windows 10 offers a stable and familiar environment for older PCs, with continued security updates and software compatibility.
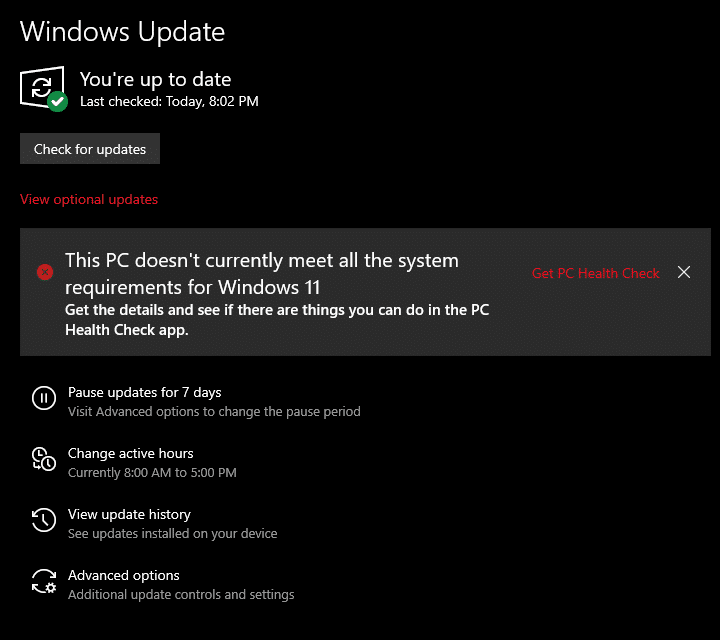
Q: How do I know if my PC meets the Windows 11 requirements?
A: Microsoft provides a PC Health Check app that analyzes your system and determines if it meets the minimum requirements for Windows 11.
Q: What are the best alternatives to Windows 11 for older PCs?
A: Linux distributions, such as Ubuntu and Fedora, and Chrome OS are popular alternatives that offer a stable and resource-efficient experience for older PCs.
Tips for Maximizing Performance on Older PCs with Windows 11
1. Optimize System Settings: Enhance Performance and Efficiency
Adjusting system settings, such as disabling unnecessary startup programs and reducing visual effects, can improve performance and efficiency on older PCs running Windows 11.
2. Manage Disk Space: Ensure Ample Space for Optimal Functioning
Regularly manage disk space by deleting unnecessary files, uninstalling unused applications, and using cloud storage to free up space for optimal system performance.
3. Keep Drivers Updated: Enhance Compatibility and Stability
Ensure that all drivers are up-to-date, as outdated drivers can contribute to compatibility issues and system instability.
4. Use Lightweight Applications: Minimize Resource Consumption
Opt for lightweight applications that consume fewer system resources, minimizing the strain on older PCs and improving performance.
Conclusion: Embracing a Balanced Approach
The decision to upgrade to Windows 11 on an older PC requires careful consideration, weighing the potential benefits against the compatibility limitations. While Windows 11 offers a sleek new interface and enhanced features, its hardware requirements necessitate a balanced approach. Users with older PCs should consider staying with Windows 10, upgrading hardware, or exploring alternative operating systems to ensure a stable and efficient computing experience. Ultimately, choosing the right path depends on individual needs, priorities, and the specific capabilities of their PC.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating the Compatibility Landscape: Why Windows 11 May Not Be Ideal for Older PCs. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!