Navigating Memory Constraints in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Navigating Memory Constraints in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Navigating Memory Constraints in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Navigating Memory Constraints in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide
![[8 Ways] Open Windows 11 Memory Diagnostic Tool for Memory Test? - MiniTool](https://www.minitool.com/images/uploads/news/2022/03/open-windows-11-memory-diagnostic/open-windows-11-memory-diagnostic-1.png)
Windows 11, like any operating system, relies heavily on system memory (RAM) to function smoothly. When the available RAM becomes insufficient to handle the demands of running programs and processes, the system encounters a state known as "out of memory." This can manifest in various ways, from sluggish performance to application crashes, ultimately hindering user experience.
Understanding the Causes of Memory Pressure
The "out of memory" situation arises when the operating system attempts to allocate more memory than is physically available. This can occur due to several factors:
- Excessive program usage: Running multiple resource-intensive applications simultaneously, such as video editing software, gaming platforms, or web browsers with numerous open tabs, can strain system memory.
- Background processes: Windows 11 runs numerous background processes, including system services, updates, and antivirus software, all of which consume memory. These processes may become particularly demanding if they are outdated or misconfigured.
- Insufficient RAM: The amount of RAM installed in a computer directly limits the number of programs and processes that can run simultaneously. Systems with limited RAM are more susceptible to memory pressure.
- Memory leaks: Some programs may contain bugs or defects that cause them to consume increasing amounts of memory over time, leading to a gradual depletion of available resources.
- Hardware failures: Faulty RAM modules can lead to memory instability and errors, hindering the operating system’s ability to manage memory effectively.
Symptoms of Memory Pressure in Windows 11
Recognizing the symptoms of memory pressure is crucial for addressing the issue promptly. Common indicators include:
- Slow system performance: Applications respond sluggishly, and the overall system feels sluggish and unresponsive.
- Frequent application crashes: Programs may unexpectedly close or freeze, indicating that they are unable to allocate sufficient memory to operate.
- Blue Screen of Death (BSOD): This error message often signifies a critical system failure, and memory pressure can be a contributing factor.
- Increased disk activity: As the system attempts to compensate for insufficient RAM, it may resort to using hard drive space as virtual memory, leading to increased disk activity and slower performance.
Addressing Memory Pressure in Windows 11
Once the symptoms of memory pressure are identified, it is essential to take appropriate steps to alleviate the situation. Several strategies can be employed:
1. Optimizing System Resources:
- Close unnecessary programs: Identify and terminate any applications that are not actively being used. This frees up memory for essential processes.
- Manage background processes: Use the Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc) to identify and disable unnecessary background processes or services. Be cautious, as disabling critical system services can impact system stability.
- Limit browser tabs: Close unnecessary browser tabs to reduce the memory footprint of web browsing. Consider using a browser extension that suspends inactive tabs to conserve memory.
- Disable unnecessary visual effects: Deactivate visual effects like animations and transparency in the System Settings to reduce the load on the graphics processing unit (GPU) and free up system resources.
2. Increasing Available Memory:
- Upgrade RAM: If the system has limited RAM, consider upgrading to a larger capacity. This directly increases the available memory for running programs and processes.
- Optimize virtual memory: Windows 11 uses a portion of the hard drive as virtual memory when physical RAM is exhausted. Adjust the virtual memory settings to ensure sufficient space is allocated, but be mindful that relying heavily on virtual memory can impact performance.
3. Troubleshooting and Repairing:
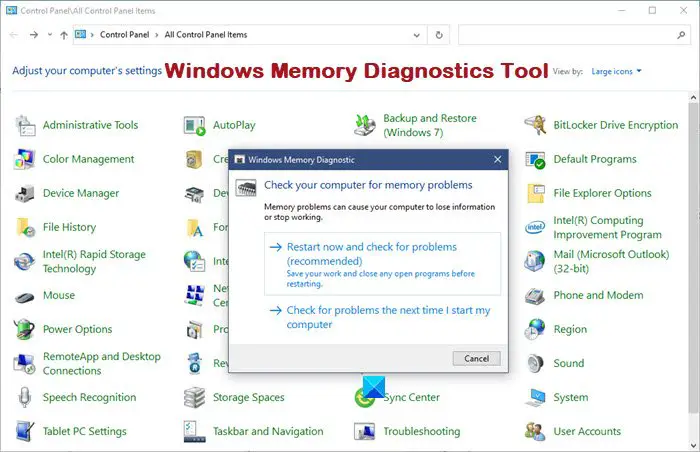
- Run a memory diagnostic test: Use the Windows Memory Diagnostic tool to check for faulty RAM modules.
- Scan for malware: Malicious software can consume significant system resources. Run a comprehensive antivirus scan to detect and remove any threats.
- Update drivers: Outdated or corrupted drivers can cause memory conflicts and instability. Ensure all drivers are up to date.
- Reinstall Windows: If all other troubleshooting steps fail, reinstalling Windows can resolve underlying issues and restore the system to a clean state.
FAQs on Memory Pressure in Windows 11
1. Why does my computer slow down when I have a lot of programs open?
Running multiple programs simultaneously puts a strain on the available system memory. When the system runs out of physical RAM, it relies on virtual memory, which is significantly slower, leading to performance degradation.
2. What is the best way to check how much RAM I have?
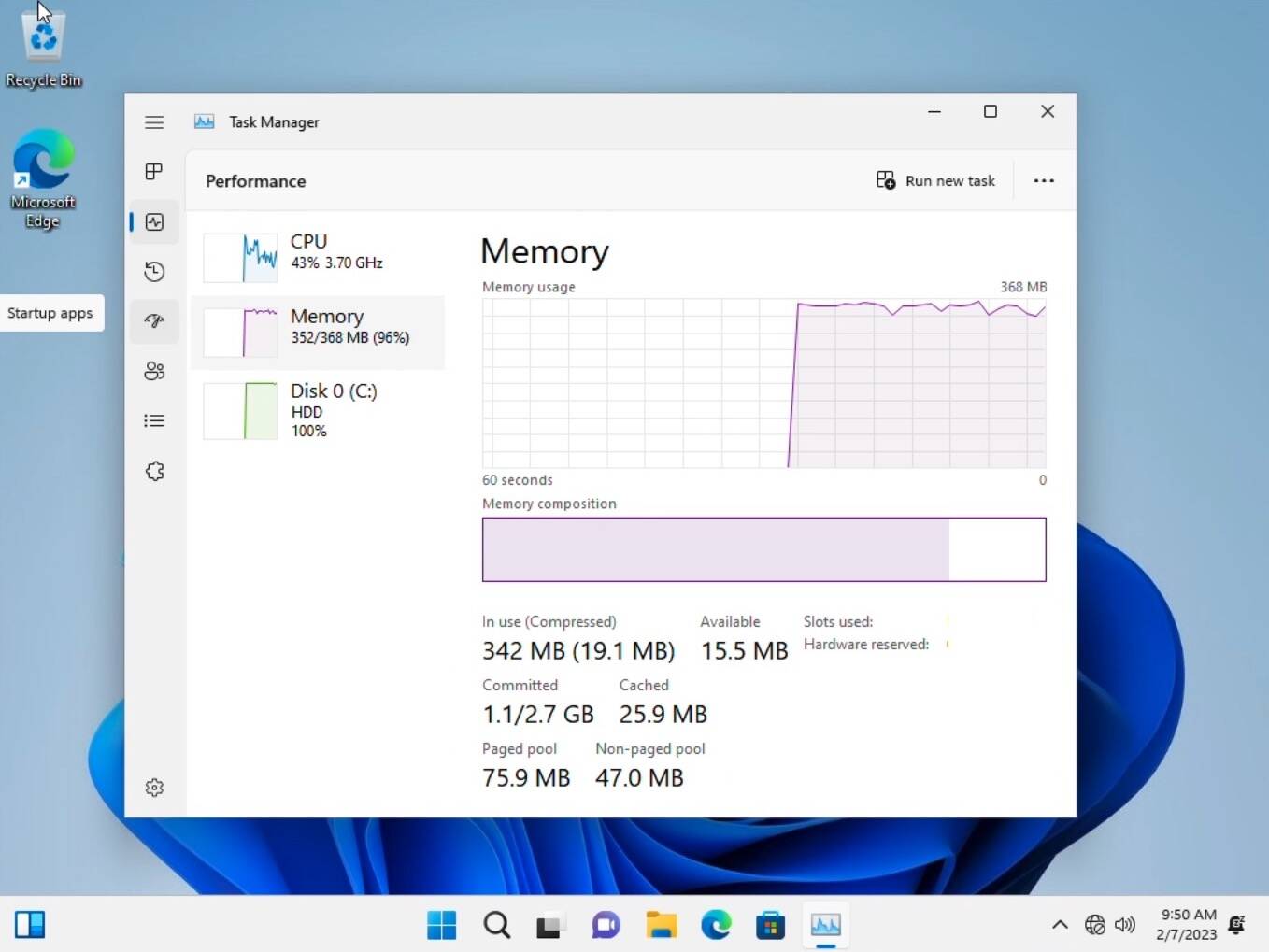
You can access system information, including RAM details, by right-clicking the "This PC" icon and selecting "Properties." Alternatively, you can open the Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc) and navigate to the "Performance" tab.
3. Can I use a USB drive as extra memory?
While some software solutions claim to use USB drives as additional RAM, this is not a true solution. These programs typically create a virtual memory file on the USB drive, which can be significantly slower than using hard drive space.
4. Is it safe to disable background processes?
Disabling background processes can free up memory, but it is crucial to be cautious. Disabling essential system services can impact system stability and functionality. Only disable processes that are identified as unnecessary or resource-intensive.
5. How can I prevent memory leaks in Windows 11?
Memory leaks are often caused by software bugs. Keep your programs updated to benefit from bug fixes and performance improvements. If a specific program is suspected of causing leaks, consider reinstalling or seeking alternative solutions.
Tips for Managing Memory in Windows 11
- Monitor memory usage: Regularly check the Task Manager to observe memory usage and identify resource-intensive processes.
- Optimize startup applications: Disable unnecessary applications from starting automatically at system startup to reduce the initial memory load.
- Use memory-efficient alternatives: Consider using lightweight software alternatives for tasks that are not critical to performance.
- Regularly clean up temporary files: Delete temporary files and browser cache to free up disk space and improve system performance.
- Consider using a memory optimizer: While not a guaranteed solution, memory optimization tools can help manage and allocate memory more efficiently.
Conclusion
Memory pressure in Windows 11 is a common issue that can significantly impact system performance and user experience. By understanding the underlying causes, recognizing the symptoms, and implementing appropriate solutions, users can effectively manage memory constraints and ensure a smooth and efficient computing environment. Regular system maintenance, proactive resource management, and timely updates are crucial for maintaining optimal system performance and avoiding memory-related issues.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Navigating Memory Constraints in Windows 11: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!